This episode of CRACKCast covers Rosen’s Chapter 25, Dyspnea. Dyspnea has a broad differential; to list them all would leave you short of breath. This episode covers an approach to dyspnea and the critical diagnoses to remember for this cardinal presentation.
Shownotes – PDF Here
[bg_faq_start]Rosen’s in Perspective
“Dyspnea”: uncomfortable sensation of breathlessness, “Air hunger”
- Non-specific spectrum from mild disease to severe disease
- May be referred to as different terms
Other terms to know:
Tachypnea − RR > normal >45-60 bpm in neonates; to >18 bpm in adults
Hyperpnea – Greater than normal minute ventilation to meet metabolic requirements
Hyperventilation – Minute ventilation exceeding metabolic demand
-> ABG showing normal PaO2
+ Uncompensated respiratory alkalosis
+ Elevated pH
Dyspnea on Exertion (DOE) – Dyspnea provoked by physical effort
Orthopnea – Dyspnea in a recumbent position
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea (PND) – Sudden SOB at night
Pathophysiology
- Normal breathing controlled by:
- Centrally by the respiratory centres in the medulla oblongata
- Peripherally by the chemoreceptors in the carotid bodies
- Mechanical centres in the diaphragm and skeletal muscles
- Any imbalance in these sites leads to dyspnea – mechanism not fully understood
Perception of dyspnea relates to:
- Increased lung resistance
- COPD or Asthma
- Increased respiratory drive
- Severe hypoxemia, acidosis, centrally acting toxins, or CNS events
1) List 10 critical causes of dyspnea
First key question:
- Is the dyspnea cardio-pulmonary OR toxic-metabolic?

CRITICAL CAUSES:
Pulmonary
- Airway obstruction
a) Heimlich maneuver & direct laryngoscopy with McGill forceps - Pulmonary embolism
- Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- Anaphylaxis
- Respiratory failure
- Tension pneumothorax +/- flail chest
a) Severe respiratory distress, hypoxia, hypotension
b) Decreased breath sounds, oxygen desaturation
Cardiac
- Pulmonary edema (due to CHF)
- Myocardial infarction
- Cardiac tamponade
Other
- Toxic ingestions (e.g. organophosphate ingestion)
- DKA
- Epiglottitis
- CO poisoning
- Acute chest syndrome (e.g. Sickle cell)
CVA / intracranial catastrophe
[bg_faq_end]Wisecracks
[bg_faq_end][bg_faq_start]1) Outline your approach to the acutely dyspneic patient
Management and disposition
- Dyspnea requires simultaneous evaluation and management
- Use the MOVIE approach and initiate empiric treatments based on:
- Trauma
- Anaphylaxis
- Foreign body
- Infectious causes
- Cardiac causes (dysrhythmia, ischemic, CHF)
- PE
- Asthma / COPD
- Use the MOVIE approach and initiate empiric treatments based on:
Signs & Ancillary Studies
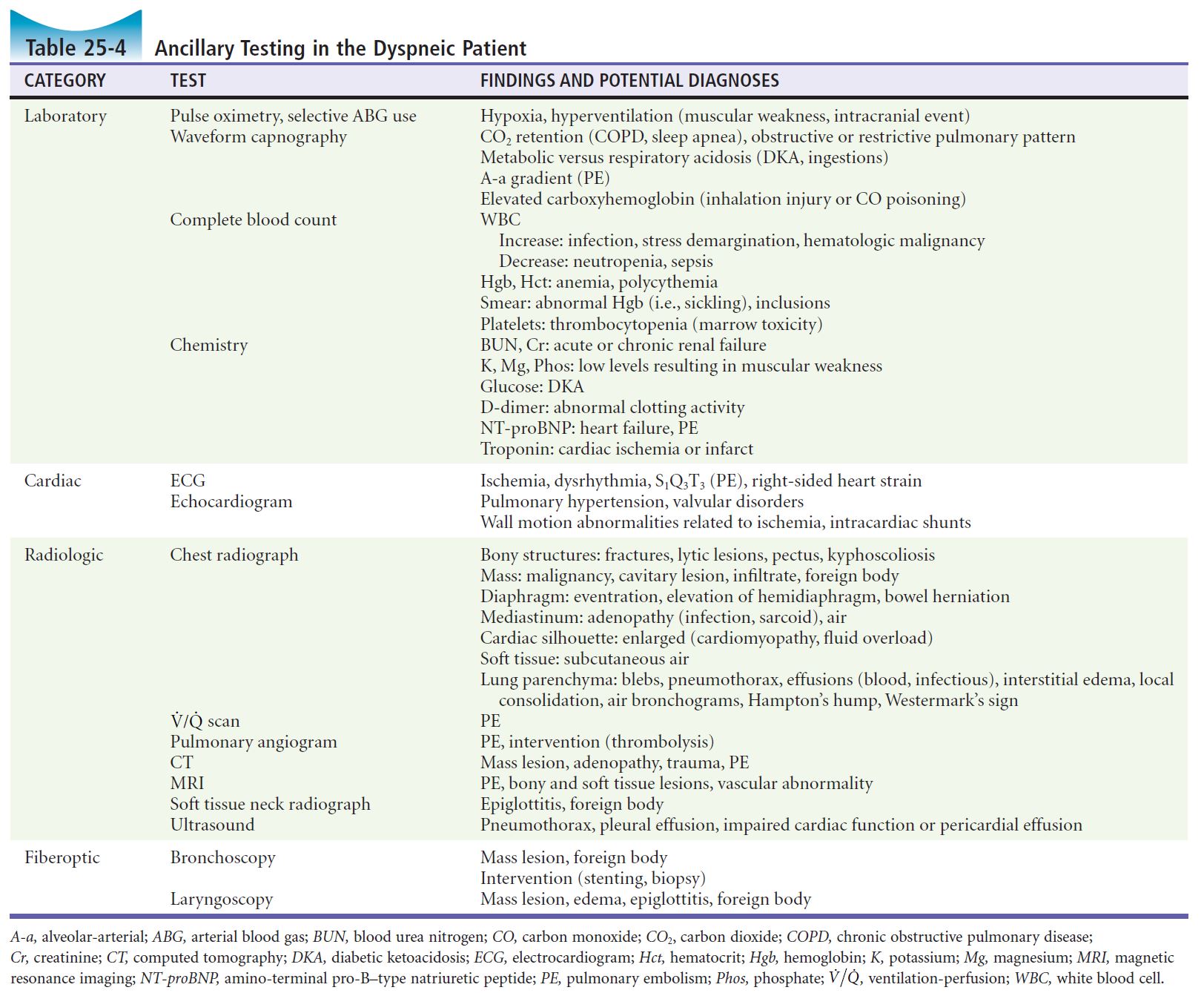
Full set of vitals, patient’s general appearance, skin/nail findings
- Neck, lung, chest, cardiac, extremities and neuro exam can assist with diagnosis
- Tests to consider:
- Vitals with SPO2 however know when it is unreliable
- ABG
- ECG
- Beside U/S
- CXR
- Labs – rule out anemia, infection, electrolyte abnormalities, or renal failure
- WBC is of little sensitivity or specificity
- BNP, troponin, and D-dimer may be of some use
- Soft tissue lateral neck – for upper airway processes
- CT chest for intra-thoracic causes (PE, pneumonia, etc.)
2) Name at least 6 uncommon causes of dyspnea
- Valvular heart disease
- Cardiomyopathy
- Mechanical interference (pregnancy, ascites, obesity, hiatal hernia)
- Ruptured diaphragm
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Guillain-Barre syndrome
- Tick paralysis
- MS
- ALS
- Polymyositis
- Porphyria
This episode was edited and uploaded by Colin Sedgwick (@colin_sedgwick)


